Figure AI’s Helix 02 Brings Full-Body Control to Humanoid Robots
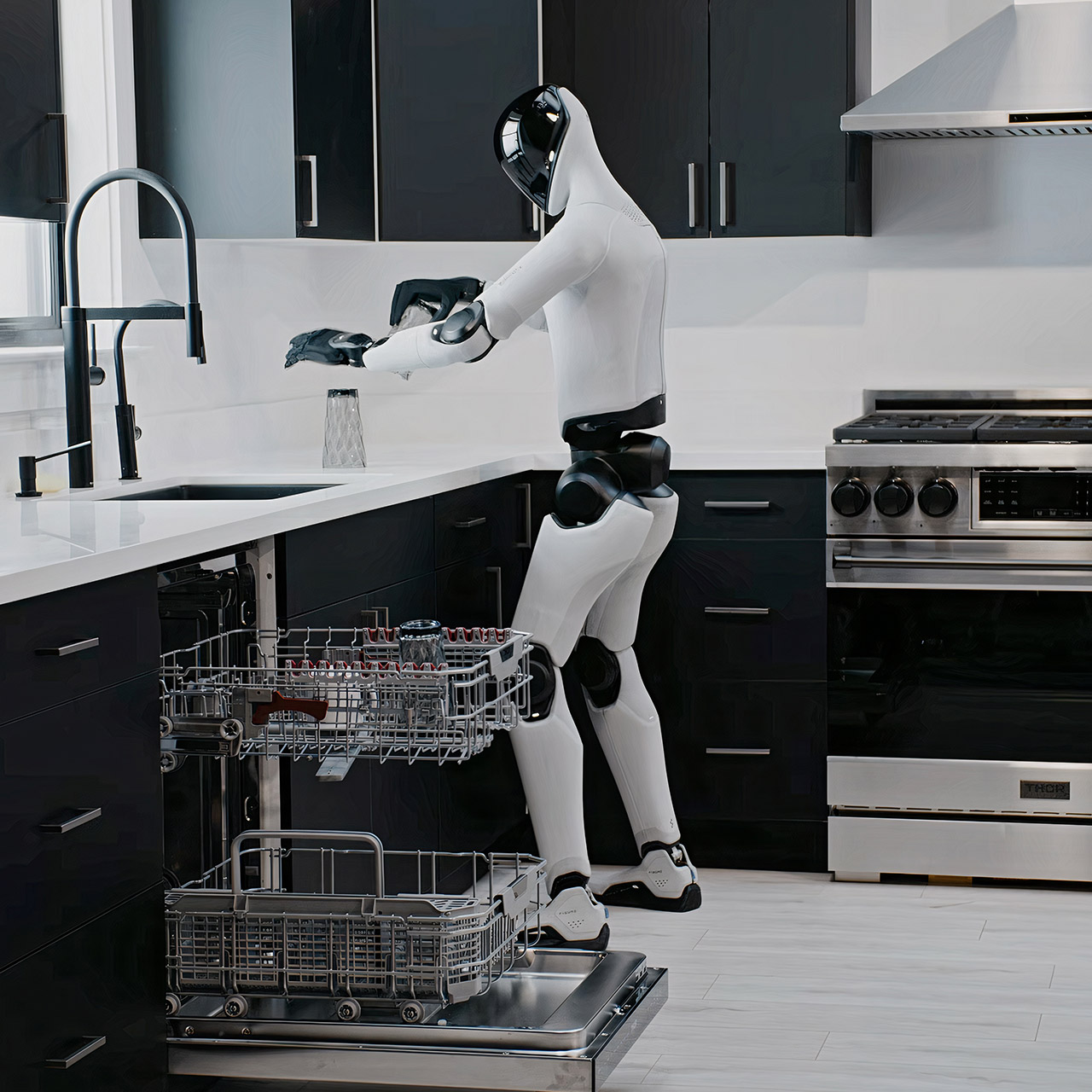


Figure AI has just released Helix 02, a revolutionary neural network that enables a humanoid robot to move from its head to its toes. With a single AI system in command, Helix 02 handles everything from going into a room to precisely grabbing objects, as well as maintaining balance while juggling difficult tasks, all based on what the robot sees through its cameras, feels through its touch sensors, and understands about its joints.
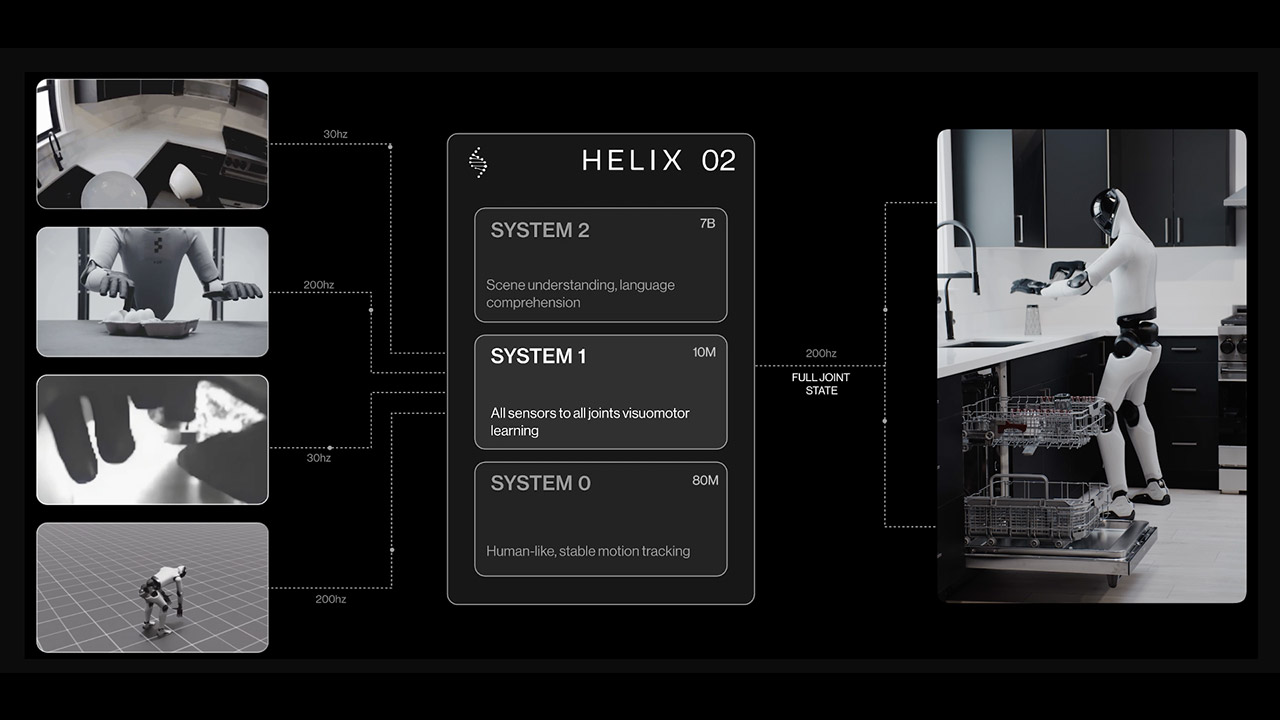
Helix 02 is a significant upgrade from the previous Helix model, which merely monitored the upper body and translated visual inputs into arm and hand movements. This time, Helix 02 pushes it a lot further. A new piece of the jigsaw, System 0, has been added to the existing arrangement of Systems 1 and 2. The ultimate result is a comprehensive chain that connects high-level decisions all the way to the quick-fire motor commands that propel the robot forward. System 2 evaluates what it sees and hears, determining what needs to happen next. System 1 then analyzes the images from the head and palm cameras, combines them with data from the robot’s touch-sensitive fingertips and overall body position, and generates target joint positions 200 times per second to keep the robot in sync. System 0 operates at an even faster rate, 1000 times per second, and takes those joint targets to generate the actual signals required to maintain the robot steady and coordinated.

Unitree G1 Humanoid Robot(No Secondary Development)
- Height, width and thickness (standing): 1270x450x200mm Height, width and thickness (folded): 690x450x300mm Weight with battery: approx. 35kg
- Total freedom (joint motor): 23 Freedom of one leg: 6 Waist Freedom: 1 Freedom of one arm: 5
- Maximum knee torque: 90N.m Maximum arm load: 2kg Calf + thigh length: 0.6m Arm arm span: approx. 0.45m Extra large joint movement space Lumbar Z-axis…

The real game changer with System 0 is that it was trained utilizing over 1,000 hours of recorded human movements, then adjusted to fit the robot’s joints and taught via simulated reinforcement learning across thousands of virtual worlds. By doing this in a controlled environment, the team avoided having to manually change the robot when it went into real-world use, which was a significant improvement over the previous approach, which relied on 100,000 lines of hand-written code and a slew of strict restrictions. Instead, scientists developed a considerably more compact 10-million-parameter neural network capable of learning the intricacies of natural motion patterns.
As a result, the robot is capable of handling day-to-day duties with ease. They demonstrated a whole kitchen cycle in which the robot moved to the dishwasher, used its foot to lever the door open, pulled out the racks, unloaded soiled dishes while keeping them steady, loaded fresh ones, and reloaded the clean ones. The entire sequence took four minutes without a pause, with 61 different motions weaved together without assistance from outside. The robot was even able to change on the go, such as closing a drawer with its hip while carrying something in its hands or shifting its stance to obtain a better grip on something fragile.
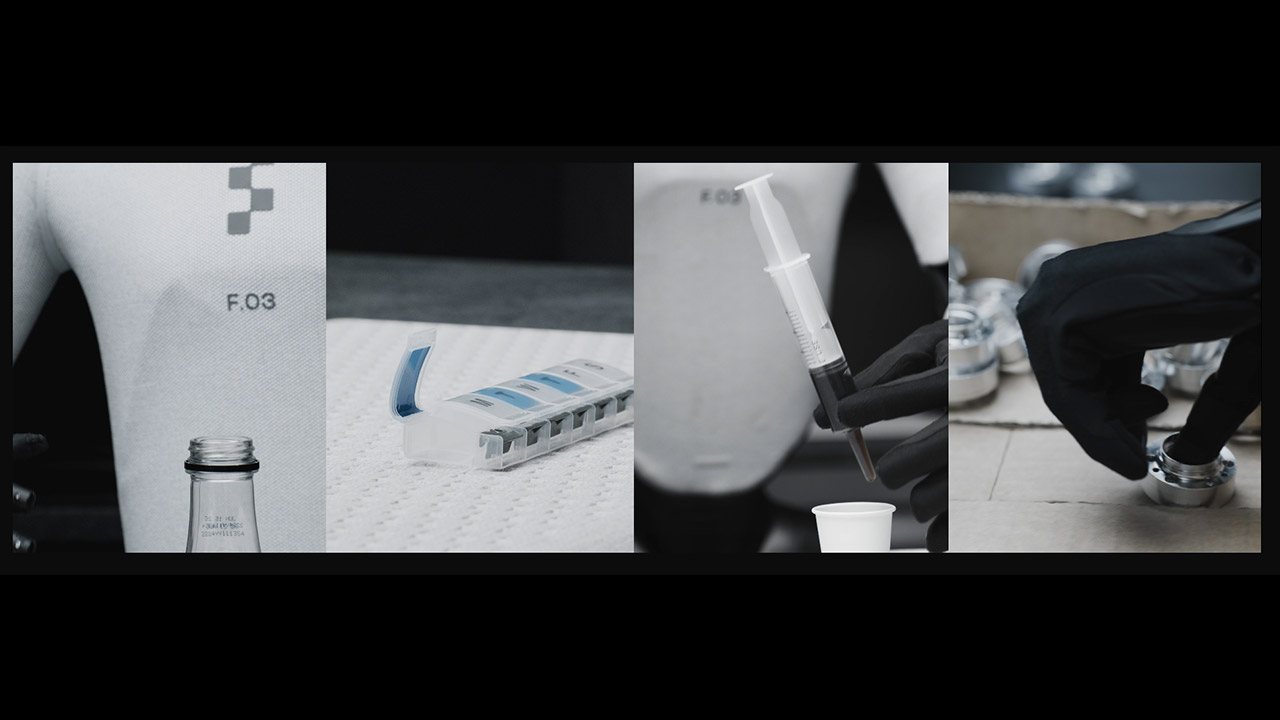
Some of the finer things it can perform are rather impressive. The system can take pills from a table using only the images from the palm views, and it recognizes when it has made contact by gentle touch input. It has the ability to utilize a syringe to precisely measure and dispense liquid. It can even extract small pieces from cluttered bins by carefully picking what it sees visually and then testing for texture. Bottle lids are easily removed because to the robot’s ability to exert exactly the correct amount of torque without slipping up.

The key to making all of this work is the combination of palm cameras and sensors on the fingertips, which can sense forces as little as three grams, allowing the robot to manage difficult views or sensitive pressure without relying on distant head-mounted cameras. Because it is all part of a single cohesive network, the robot can scale from little modifications to full-fledged strides across a room.
Figure AI’s Helix 02 Brings Full-Body Control to Humanoid Robots
#Figure #AIs #Helix #Brings #FullBody #Control #Humanoid #Robots







